(Na = 23.0 C = 12.0 O = 16.0)
Calculate:
(a) Moles of Nitric acid used
(b) Moles of sodium carbonate in 25cm of the solution
(c) Mass of unknown sodium carbonate used
2. Element A has atomic mass 23 and element B has atomic mass 7 and also have 12neutorns and 4 neutrons respectively.
(a) Write the electronic arrangement of A and B
(b) Which element has higher ionization energy? Explain
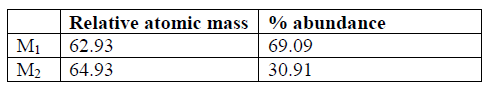
3. The table below shows the relative atomic masses and the percentage abundance of isotope M1 and M2 of element M. Calculate the relative atomic mass of element M
4. (a) Element V has two isotopes. Two thirds of V and one third of V . What is the relative atomic mass of element V?
(b) The following refers to element Y Given that isotope C contains 31 neutrons in its nucleus find the number of protons in isotope B
5. The table below shows the relative atomic masses and the percentage abundance of the isotopes L1 and L2 of element L. Calculate the relative atomic mass of element K.
6. An element M has two isotopes M and M . The relative atomic mass of the naturally occurring is 63.55. Calculate the percentage of each isotope
7. An oxide of element G has the formula as G2O3
(a) State the valency of element G
(b) In which group f the periodic table is element G?
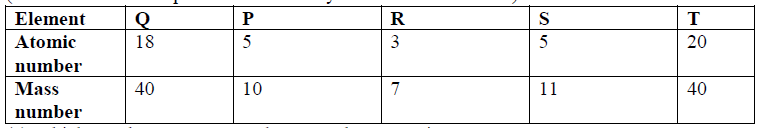
8. The table below gives information about the ions T+ and Z2- (a) How many protons are there in the nucleus of ?
(i) Element T?
(ii) Element Z?
(b) Determine the relative formula mass of the compound formed between T and Z
(c) State two conditions under which the compound would conduct electricity
9. Carbon and silicon belong to the same group of the periodic table, yet Carbon (IV) oxide is a gas while silicon (IV) oxide is a solid with a high melting point. Explain this difference
10. An ion of oxygen is larger than oxygen atom. Explain
11. Copper (II) oxide and charcoal are black solids. How would you distinguish between the two solids?
12. (a) Element X is found in period III and group IV. It consists of two isotopes 28X and QX. A sample of X was found to consist of 90% of 28X.If the relative atomic mass of X is 28.3, work out the number of neutrons in QX
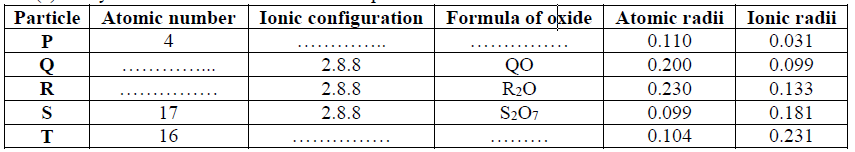
(b) Draw an electrochemical cell for the above cell
13. Study the table below and answer the questions that follows:- (Letters are not the actual
symbols of element)
14. Define the term melting point of a substance
15. Use the information in the table below to answer the questions that follow. (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements).
(b) Give the number of neutrons in an atom of element R
16. The table below gives some elements in the periodic table. Use it to answer the questions that Follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements. Which of the above letters represent:
a) A metallic element which forms ions with the smallest ionic radius? Explain
b) A non metallic element with the largest bbatomic size? Explain
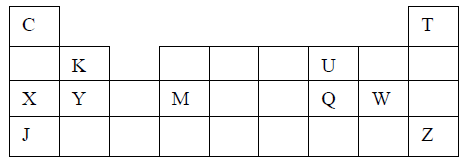
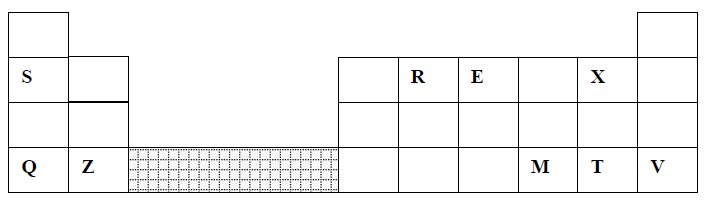
17. The grid below is part of the periodic table. Use it to answer the questions that follow: (The letters are not the actual symbols).
b) Which element has the same electron arrangement as the stable ion of:
(i) F ……………………………. (ii) A ……………………..
c) Element Q has atomic number 15. Indicate its position on the grid.
d) Explain how the atomic radii of the following compare:
(i) C and F
(ii) C and D
e) Write the type of bond present in a compound formed between D and A.
f) Compound C and G were completely burned in oxygen.
(i) Write down equations to show the combustion of each of the elements.
(ii) State whether each of the oxides (i) above is basic or acidic.
d) Explain how the atomic radii of the following compare:
(i) C and F
(ii) C and D
e) Write the type of bond present in a compound formed between D and A.
f) Compound C and G were completely burned in oxygen.
(i) Write down equations to show the combustion of each of the elements.
(ii) State whether each of the oxides (i) above is basic or acidic.
18. The following flow chart shows the industrial manufacture of Nitric (V) acid.
a) Identify substance B, C, E and F.
b) Describe what happens in the catalytic chamber.
d) 60 – 65% nitric (V) acid is produced in the absorption chamber. Describe how the acid can be concentrated.
e) State why nitric (V) acid is stored in dark bottles.
f) Copper reacts with nitric (V) acid and not hydrochloric acid. Explain.
19. The number of protons, neutrons and electrons in atoms A to F are given in the table below
the letters do not represent the actual symbol of the elements:-
(i) An atom of a metal ..........................................................
(ii) A neutral atom of a non-metal ........................................
(iii) An atom of a noble gas ..................................................
(iv) A pair of isotopes ............................................................
(v) A cation ...............................................................................
(b) The grid below shows a part of the periodic table. The letters do not represent the actual
symbols.
Use it to answer the questions that follow:- (a) How do the atomic radius of element X and Y compare
(b) (i) Using crosses (X) to represent electrons, draw the atomic structure of element Q
(ii) State the period and the group to which element Q belong
(c) (i) The ionic configuration of element G is 2.8 G forms an ion of the type G-1.
Indicate on the grid, the position of element G.
(ii) To which chemical family does element G belong?
(iii) State one use of element U
(iv) What is the nature of the compound formed between K and U
20. (a) Study the table below and answer the questions that follow. (i) Complete the table above
(ii) From the table, choose the most reactive metal. Explain
(iii) Which element is the most electronegative. Explain
(iv) Using dots (.) and crosses (x) to represent electrons, show the bonding in the chloride of Q
(v) Explain the solubility of element T in water
(b) (i) Why is aluminium used to make utensils yet it is a reactive metal?
(ii) Distinguish between valency and oxidation number
21. a) Work out the oxidation number of phosphorous in the following compound H3PO3
b) Study the equation below:
22. The grid below represents part of the periodic table. The letters do not represent the actual
symbols of the elements. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
(b) State the name of the chemical family to which P and Q belong
(c) Write the formula of the compound formed between P and V
(d) Compare the melting points of Q and S. Explain
(e) Identify an element whose oxide dissolves in both acids and alkalis
(f) Write the equation for the burning of T in excess air
(g) Using dots (•) and cross (x) to represent electrons, draw a diagram to illustrate bonding in the sulphide of Q
(h) State one use of element X
23. The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
(ii) Which of the metal is most reactive? Explain
(iii) What name is given to the family of elements to which elements X and T belong?
(iv) Explain why:-
(I) Ionic radius of Q is larger than that of M
(II) Atomic radius of Q is greater than that of S
(v) Which of the element in the table does not have the ability to form an ionic or covalent bond? Explain
(vi) Give the formula of the compound formed between R and Z
24. The grid below is part of the periodic table. The elements are not represented by their actual symbols. Use the information to answer the questions that follow.
(I) Non — metal?
Explain
(II) Metal?
Explain
(ii) Name the family to which elements T and Q belongs.
(iii) Write the formula of the compound formed when W reacts with S.
(iv) Name the type of bond and structure formed when elements R and K react.
(v) Explain why element N doesn’t form compounds with other elements.
(vi) Compare the atomic radii of T and Q. Explain.
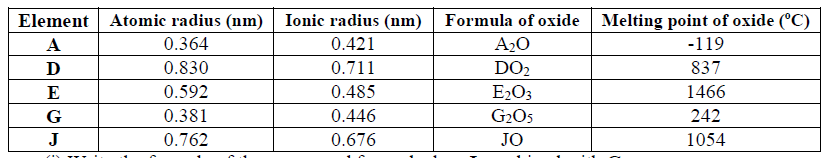
25. Study the data given in the following table and answer the questions that follow. The letters
are not the actual symbols of elements.
(ii) Explain why the melting point and boiling points of element D is the highest
(iii) Explain why the element represented by letter E has two melting point values
(iv) Write down the chemical formula between element C and sulphate ions
(v) Name the chemical family in which H belong and state one use of the element
(vi) What is the nature of the oxide of the elements represented by letters C and F?
26. An element W has an atomic number 13.
a) Write the electronic configuration of the most stable ion of W
b) Write the formula of the oxide of the element W
27. Identify the particles that facilitate the electric conductivity of the following substances
(i) Sodium metal
(ii) Sodium Chloride solution
(iii) Molten Lead Bromide
28. Compare with a reason the atomic radius of Sodium to that of Aluminum.
29. Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow:
b) Give the group and period to which elements Q and R respectively.
Q ……………………………………………………
R ……………………………………………………
30. Ethanol is a liquid at room temperature but does not conduct electricity. Explain.
31. Electronic configuration for elements represented by P, Q, R and S are:-
P= 2.8.6, Q= 2.8.2, R= 2.8.1 D= 2.8.8.
(a) Select the element which forms
(i) A double charged ion
(ii) A soluble carbonate
32. The table below gives information on four elements by letters K, L, M and N. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbol of the elements.
(b) What is the most likely formula of the oxide of L?
(c) Which element is non-metal? Explain
33. Study the information given below and answer the questions that follow:
(b) Explain why the melting point of the oxide of E is higher than that of the oxide of G























No comments:
Post a Comment