Thursday, 29 August 2019
Joining KUPPET
~Are you willing to join KUPPET?
~ Are you paying agency fee and would like to join KUPPET?
~ You are in KNUT and you have made the decision to join KUPPET?
Do not wait lose your salary and be taken back to salary scale of 2016. By joining KUPPET you have will made the right choice of continuing to gain the benefits of the current CBA.
*TO JOIN KUPPET FOLLOW THIS PROCEDURE*
1. Log in to Payslips online
2. Go to *Send payslip to third party*
3. On category, select *SWA.*
4. On Company, select *KUPPET UNION DUES*
5. Then *Click or Press send payslip*
6. After successfully sending your payslip to KUPPET Union Dues *SMS/ WhatsApp your TSC NO and Name to 0723839280 (Mr. Kimotho)*
*TO WITHDRAW FROM KNUT*
1. Log in to TSC online Payslips.
2. Go to third Party Section 3. Go to UNION MEMBER VALIDATION
4. Press the small box on the far right against KNUT
5. Press Stop Union Membership button.
*NOTE*
After successfully sending payslip, please Send your *TSC NO and Name to 0723839280 (Mr. Kimotho)* for onward transmission to Nairobi for immediate processing.
Thursday, 22 August 2019
Census questions you will be asked when the exercise begins
- What are the names of each person who spent the night of 24th/25th August, 2019 in this household?
- What is each person’s relationship to the head of this household?
- What is their sex ?
- What is their age (s)?
- What is their date of birth?
- Please insert line number of their biological mother
- Is the person a usual member of this household?
- What is their ethnicity or nationality ?
- What is their religion ?
- What is their marital status?
- Where were they born?
- Where were they living in August 2018?
- When did they move to the current county?
- Why did they move to the current place of residence?
- How many children have you ever borne alive?
- How many children have you borne alive who usually live in this household ?
- How many children have you borne alive who usually live elsewhere ?
- How many children have you borne alive who have died ?
- When was your last child born?
- Where did this last birth occur?
- What was the sex of this child/ children?
- Was this last birth notified?
- Is this last child/ children still alive ?
- If the last child is not alive, when did the child die?
Tuesday, 13 August 2019
Chemical families
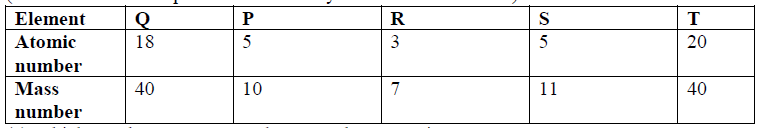
1. Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow:
2 State the reason for using Argon in electric light bulbs
3. Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
(a) What is the general name given to the group in which the elements X, Y and Z belong?
(b) Select two elements which are coloured gases
(c) Explain why Z has the highest boiling point
(d) Write an equation for the reaction of element Z with iron metal
(e) Element Y was dissolved in water and a piece of blue litmus paper was put into the resulting solution. State and explain the observation that was made on the litmus paper
4. The table below shows elements A, B, C, E, F, and G. Elements in group X have a valency of 2 while elements in group Y have a valency of 1. Use the table to answer the questions that follow:- (i) Atomic radius increases from A to C and from E to G. Explain
(ii) Explain the difference in the atomic and ionic radii of group X elements
(iii) Elements C and G belong to the same period. Explain why the atomic radius of C is greater than that of G
(iv) Give the formula of the compound formed when B and F react
(v) What type of bonding is formed in the compound above? Explain
(vi) Starting with the least reactive, arrange the elements in group Y in the order of reactivity. Explain:
5. The information in the table below relates to elements in the same group of the periodic table.
Study it and answer the question that follows.
Which element has the highest ionization energy? Explain
6. Starting with Lead (II) carbonate explain how you would prepare a pure sample of Lead (II) sulphate
7. a) What is an isotope?
b) An element Q consists of 3 isotopes of mass 28, 29, 30 and percentage abundance of 92.2, 4.7, 3.1 respectively. Determine the relative atomic mass of the element?
8. Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow. (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements)
(a) What is the general name given to the group in which elements P, Q and R belong?
(b) Explain why P has the highest ionization energy
(c) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between element Q and water
(a) Would these form part of a metallic or a non-metallic group? Explain
(b) Suggest an element in the table above likely to be the most reactive. Explain
(b) Suggest an element in the table above likely to be the most reactive. Explain
2 State the reason for using Argon in electric light bulbs
3. Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements.
(b) Select two elements which are coloured gases
(c) Explain why Z has the highest boiling point
(d) Write an equation for the reaction of element Z with iron metal
(e) Element Y was dissolved in water and a piece of blue litmus paper was put into the resulting solution. State and explain the observation that was made on the litmus paper
4. The table below shows elements A, B, C, E, F, and G. Elements in group X have a valency of 2 while elements in group Y have a valency of 1. Use the table to answer the questions that follow:- (i) Atomic radius increases from A to C and from E to G. Explain
(ii) Explain the difference in the atomic and ionic radii of group X elements
(iii) Elements C and G belong to the same period. Explain why the atomic radius of C is greater than that of G
(iv) Give the formula of the compound formed when B and F react
(v) What type of bonding is formed in the compound above? Explain
(vi) Starting with the least reactive, arrange the elements in group Y in the order of reactivity. Explain:
5. The information in the table below relates to elements in the same group of the periodic table.
Study it and answer the question that follows.
6. Starting with Lead (II) carbonate explain how you would prepare a pure sample of Lead (II) sulphate
7. a) What is an isotope?
b) An element Q consists of 3 isotopes of mass 28, 29, 30 and percentage abundance of 92.2, 4.7, 3.1 respectively. Determine the relative atomic mass of the element?
8. Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow. (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements)
(b) Explain why P has the highest ionization energy
(c) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between element Q and water
Monday, 12 August 2019
Nitrogen and its compounds
(i) Write an equation for the reaction that takes place
(ii) Why is it necessary to have a hot nichrome wire in the gas jar?
(iii) Write the formula of the complex ion formed when excess ammonia gas is passed through
a solution containing Zn2+ ions
(ii) Why is it necessary to have a hot nichrome wire in the gas jar?
(iii) Write the formula of the complex ion formed when excess ammonia gas is passed through
a solution containing Zn2+ ions
2. The diagram below shows the catalytic oxidation of ammonia gas. Use it to answer the
questions that follow:-
(a) What metal could rod M be made of?
(b) State and explain two observations made inside the conical flask
3. Ammonia gas is prepared in the laboratory by the action of an alkali on an ammonium salt. A student wanted to prepare a sample of ammonia gas in the laboratory. (a) Give one alkali that can be used in the above experiment
(b) Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the above experiment
4. (a) Explain the importance of the high percentage of nitrogen in air
(b) Why is nitrogen used for storage of semen in artificial insemination?
5. The diagram below is used in preparation of a gas in the laboratory. Answer the questions that follow;
(b) State one physical property which makes it possible for the gas to be collected as shown
(c) State one commercial use of gas X
6 Study the flow charts below and use them to answer the questions that follow:
(i) Solution A
(ii) Solution B
(b) State and explain the observations made when a sample of dry white precipitate B is
heated in a test-tube
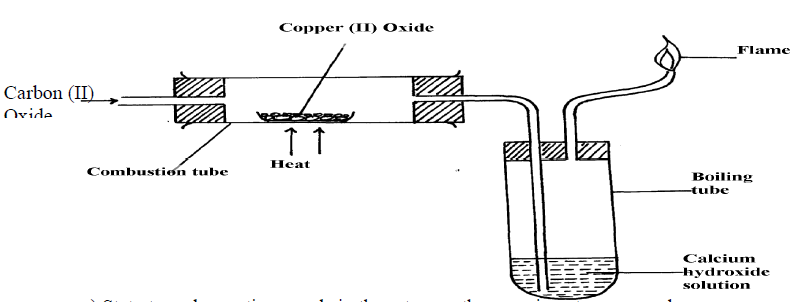
7. The set-up below is an arrangement showing how metals react with nitrogen (IV) oxide.
Study it and answer the questions that follow:-
(a) Nitrogen (IV) oxide is passed through the combustion tube before copper is heated. Give a reason for thisStudy it and answer the questions that follow:-
(b) State the observations that would be made at the end of the experiment in the combustion tube
(c) Name gas N ……………………………………………………………………..
8. (a) In haber process hydrogen and nitrogen react in the presence of finely divided iron catalyst. Explain why the catalyst is finely divided
(b) A mixture of N2, H2 and NH3 was bubbled through 0.2M hydrochloric acid solution. The final concentration of the acid was found to be 0.1M. Give explanation
9. In an experiment, a few drops of concentrated nitric acid were added to aqueous iron II sulphate in a test-tube. Excess ammonia solution was then added to the mixture
(a) State the observations that were made when:-
(i) Concentrated nitric acid was added to aqueous iron (II) sulphate
(ii) Excess ammonia was added to the mixture
(b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction which occurred in a (ii) above
10. The chart below shows a summary for the preparation of nitrogen gas from air
(b) Write an equation for the reaction taking place in chamber II
(c) The nitrogen gas obtained is not pure. Explain
11. Dilute nitric acid is added to excess green solid. Effervescence occurs and a blue solution is formed. When excess ammonia solution is added to a sample of the solution a deep blue solution is formed
(a) Identify the anion and cation in the green solid:
(b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction forming deep blue solution
12. The diagram below is a set-up for preparation and collection of a gas. Study it answer the questions that follow:
(ii) Write an equation for the formation of gas X
(iii) What precaution should be observed when preparing gas X by the above method?
(iv) Describe the suitable drying agent for gas X
(v) How can one confirm that the gas collected is gas X?
(vi) State two physical properties of gas X
(b) The diagram below is a set-up used in preparation of ammonia solution. Study it and answer
the questions that follow (i) What is the purpose of the filter funnel in the set-up above?
(ii) What would happen if a delivery tube was used in place of the filter funnel?
(iii) What observation would be made on litmus paper placed into the solution in the beaker at the end of the experiment?
13. The following flow chart shows the industrial manufacture of Nitric (V) acid.
a) Identify substance B, C, E and F.
b) Describe what happens in the catalytic chamber
d) 60 – 65% nitric (V) acid is produced in the absorption chamber. Describe how the acid can be concentrated.
e) State why nitric (V) acid is stored in dark bottles.
f) Copper reacts with nitric (V) acid and not hydrochloric acid. Explain.
14. The flow chart below illustrates two industrial processes, Haber process and the Contact process:
(i) Give the name of the process by which air is seperated into oxygen and nitrogen(ii) Apart from oxygen and nitrogen gases produced from process (a)(i) Name one other gas produced
(b) Name the substances represented by the letters A, B, C and E
(c) Name the catalysts used in:
(i) Haber Process ……………………………………………………………………..
(ii) Contact Process ……………………………………………………………………..
(d) Explain the role of the catalysts in both the Haber and the Contact processes
(e) Write a chemical equation for the formation of compound B
(f) Calculate the percentage by mass of the nitrogen present in compound D
(g) Give one major use of compound E
15. The diagram below represents a set-up used to obtain nitrogen from air. Study it and
answer the questions that follow:-
(ii) What is the purpose of sodium hydroxide
(iii) Write an equation for the reaction which took place in tube “P”
(iv) Give the name of one impurity in the nitrogen gas obtained
(v) Give a reason why liquid nitrogen is used for storage of semen for artificial insemination
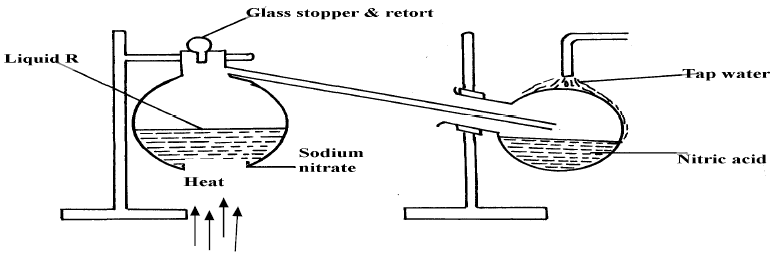
(b) The set-up below was used to prepare nitric acid.
(i) Give the name of liquid ‘R’ .........................................................................
(ii) Explain the following:-
(a) Nitric acid is stored in dark bottles
(b) The reaction between copper metal with 50% nitric acid in an open tube gives brown fumes
16. Study the flow chart below and answer the questions which follow:
(a) Nitrogen gas ………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) Hydrogen gas …………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) State three conditions required in process I
(iii) Name: catalyst P…………………………………………………………………
Gas M……………………………………………………………………..……
(iv) Write chemical equations for;
(a) Formation of gas M
(b) The reaction in the absorption tower
(v) Give two reasons why step IV is necessary
(vi) Describe how you would test if a given liquid is a nitrate
(vii) Give three uses of nitric acid
17. The diagram below shows the apparatus for the laboratory preparation of one of the oxides
of Nitrogen
(ii) Write the equation for the thermal decomposition of ammonium Nitrate
(iii) The gas is being collected over hot water. Explain
(iv) State and explain the observations made when burning sulphur is lowered into a gas jar containing the gas
(b) (i) Name the catalyst used during catalytic oxidation of ammonia
(ii) Nitrogen (IV) oxide is the final product during catalytic oxidation of ammonia. Write a chemical equation for its formation
(iii) State two physical differences between Nitrogen (I) oxide and Nitrogen (IV) Oxide
(c) Nitric acid is prepared in the laboratory by action of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid on a suitable Nitrate and distilling off the Nitric acid, in all glass apparatus.
(i) Why must the apparatus be made of glass?
(ii) Hot concentrated Nitric acid reacts with sulphur in the equation below:-
(I) Identify the species :-
Oxidised ………………………… Reduced …………………………………
(II) Pure nitric acid is colourless but the product during its preparation is usually pale yellow.
Explain
18. a) Describe the process by which oxygen can be obtained from air on large scale
b) The flow chart below shows the industrial manufacture of nitric (V) acid i) Identify substances X and Y
ii) Write an equation for the reaction taking place in the absorption tower
iii) The concentration of the acid obtained is about 60%. How can this concentration be increased to about 65%?
iv) A factory uses nitric (V) acid and ammonia as the only reactants for the production of a fertilizer. If a mass of 9600kg of fertilizer was produced, calculate the mass of ammonia gas needed
(N = 14, H = 1, O = 16) (a) Name another substance which can be used instead of sodium hydroxide
(b) What is the function of filters?
(c) Identify the substance removed at step III
(d) At what temperature does liquid oxygen distil?
(e) Identify process X
(f) Describe how process X occurs
(g) I. State one industrial use of Nitrogen
(II) Air is a mixture but not a compound. Give two reasons
20. Using chemical equations show the bleaching actions of chlorine and sulphur(IV)oxide
21. The diagram below represents an in complete set-up for preparation of a dry sample of gas R
b) Write a chemical equation for the reaction that produces gas R
22. The diagram below was used to investigate the reaction between nitrogen(I)oxide and copper
turnings. Study it and answer the questions that follow: a) What has been omitted in the set-up? (show it on the diagram)
b) Write a chemical equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube
c) State one use of gas P
23. When sulphur powder is heated to over 400oC the following changes are observed:- At 113oC it melts into light brown liquid. The liquid then darkens to become reddish-brown and very viscous at 160oC. Above 160oC the liquid becomes almost black. At the boiling point the liquid becomes mobile. Explain these observations
24. Concentrated sodium chloride (Brine) was electrolysed using platinum electrodes.
What would be the difference in terms of products at each electrode if dilute sodium chloride
solution was used in place of brine. Explain
25. (i) Nitrogen (I) Oxide supports, combustion of burning charcoal. Write an equation
to show this reaction
(ii) Ammonium nitrate can be heated to give off nitrogen (I) Oxide. However, a mixture
of NH4Cl and NaNO3 is preferred. Explain
(iii) Ammonia turns wet red litmus paper blue. Which ion is responsible for this reaction
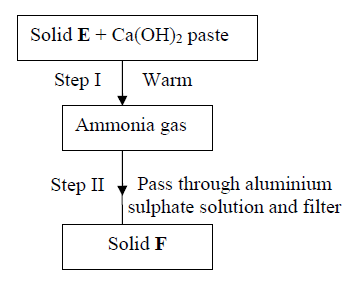
26. Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow:
(b) Write down a balanced equation for the reactions that lead to formation of solid F
27. When a few drops of aqueous ammonia were added to a colourless solution X, a white
precipitate was formed. On addition of more aqueous ammonia, the white precipitate
dissolved to a colourless solution Q
(a) Name the white precipitate formed
(b) Write formula of the complex ion present in the colourless solution Q
28. The first step in the industrial manufacture of nitric cid is the catalytic oxidation of ammonia gas.
a) What is the name of the catalyst used?
b) Write the equation for the catalytic oxidation of ammonia gas.
c) Nitric acid is used to make ammonium nitrate. State one use of ammonium nitrate.
29. Explain what is observed when ammonia gas is bubbled into Copper (II) sulphate solution till in excess.
30. (a) State the conditions under which nitrogen react with hydrogen to form ammonia during Haber process
(b) When dry ammonia gas is passed over hot copper (II) Oxide, a shinny brown residue and a colourless droplets are formed. Explain these two observations
(b) When dry ammonia gas is passed over hot copper (II) Oxide, a shinny brown residue and a colourless droplets are formed. Explain these two observations
31. Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
(b) Identify:-
(i) Gas A ………………………………………….………
(ii) Liquid B ………………………………..…………………
Carbon and its compounds
1. (a) State one use of graphite
(b) Both graphite and diamond are allotropes of element Carbon. Graphite conducts electricity whereas diamond does not. Explain
2. Below is a simplified scheme of solvay process. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
b) Write an equation for the process III.
c) Give one use of sodium carbonate.
3. A burning magnesium continues to burn inside a gas jar full of carbon (IV) oxide. Explain.
4. The diagram below shows a jiko when in use
(a) Identify the gas formed at region H
(b) State and explain the observation made at region G
5. Study the diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
(a) State the observation made in the combustion tube.
(b) Write an equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube
(c) Give one use of P
6. (a) Identify two substance that are reacted to regenerate ammonia gas in the solvary process
(b) Write down a balanced chemical equation for the reaction above
7. When the oxide of element H was heated with powdered Carbon, the mixture glowed and Carbon (IV) oxide was formed. When the experiment was repeated using the oxide of element J, there was no apparent reaction
(a) Suggest one method that can be used to extract element J from its oxide
(b) Arrange the elements H, J and Carbon in order of their decreasing reactivity
8. (i) Diamond and silicon (IV) Oxide have a certain similarity in terms of structure and bonding. State it
(ii) State one use of diamond
9. (a) What is allotropy?
(b) Diamond and graphite are allotropes of Carbon. In terms of structure and bonding
explain why graphite conducts electricity but not diamond
10. The diagram below shows a charcoal stove with different regions
(a) Write an equation for the formation of the product in region B
(b) How would one avoid the production of the product at B? Give a reason for your answer
11. Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow:
(a) Explain the observation made in the combustion tube during the experiment
(b) Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the combustion tube
12. Diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon:-
(a) What is meant by allotropes?
(b) How do they differ in their structure and bonding
13. Study the experimental set-up below:
a) State two observations made in the set up as the experiment progressed
b) By use of a chemical equation, explain the changes that occurred in the boiling tube
c) Why was it necessary to burn the excess gas?
14. The diagram below shows the heating curve of a pure substance. Study it and answer the
questions that follow:
points A and C
(d) The substance under test is definitely not water; Give a reason for this
(e) What would happen to the melting point of this substance if it were contaminated with sodium chloride?
(f) What happens to the temperature between points B and C?
15. Study the set-up below and answer the questions that follow:
(a) (i) Name Gas X ………………………………………………………………
(ii) State the effect of releasing gas X to the environment
(b) Write down equations for the reactions taking place in;
(i) Tube I
(ii) Tube II
(iii) Flask
(c) State the observation made in tube III
(d) Write down an equation for the reaction which could be used to generate Carbon
(IV) Oxide for the above set up
(e) Name the reagents used to generate gas x in the laboratory
(f) Complete the diagram above to show how excess gas x can be collected
16. The figure below shows the stages in the manufacture of sodium carbonate. Study the diagram
below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
a) (i) Name three starting materials in the manufacturer of sodium carbonate.
(ii) Which substances are recycled in this process?
(iii) Identify the chambers in which the recycled substances are regenerated.
(iv) Name the substances U and V.
b) Give an equation for the reaction which occurs:
(i) In the reaction chamber 1
(ii) When solid V is heated.
(iii) In the reaction chamber 3.
c) State one commercial use for
(i) Sodium carbonate.
17. The set-up below was used to prepare dry carbon (II) Oxide gas. use it to answer the questions
below it:
(a) (i) State two mistakes committed in the set-up arrangement above
(ii) The student produced carbon (IV) oxide gas from the reaction between Lead (II) Carbonate
and dilute hydrochloric acid. The gas was produced for a short time and the reaction came
to a stop. Explain
(iii) Write the equation for the reactions taking place in the combustion tube and the conical
flask:
Combustion tube:…………………………………………………………………..
(b)

Which property of carbon (II) Oxide is demonstrated by the above equation?
(c) Aluminium carbonate does not exist. Give a reason
(d) Ammonium carbonate decomposes when heated. Write a chemical equation to
represent this decomposition
18. State and explain the observation made when a piece of charcoal is dropped in a jar containing concentrated nitric (V) acid
19. When Carbon (IV) oxide is passed through lime water, a white precipitate is formed but when excess Carbon (IV) Oxide is passed, the white precipitate disappears;
(a) Explain why the white precipitate disappears
(b) Give an equation for the reaction that takes place in (a) above
20. The set-up below was used to prepare a carbon (II) oxide gas.
(a) Give the name of substance A ………………………………………………………….
(b) Complete the diagram to show how the gas can be collected
(c)Write the equation for the reaction
(b) Both graphite and diamond are allotropes of element Carbon. Graphite conducts electricity whereas diamond does not. Explain
2. Below is a simplified scheme of solvay process. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
b) Write an equation for the process III.
c) Give one use of sodium carbonate.
3. A burning magnesium continues to burn inside a gas jar full of carbon (IV) oxide. Explain.
4. The diagram below shows a jiko when in use
(a) Identify the gas formed at region H
(b) State and explain the observation made at region G
5. Study the diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
(a) State the observation made in the combustion tube.
(b) Write an equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube
(c) Give one use of P
6. (a) Identify two substance that are reacted to regenerate ammonia gas in the solvary process
(b) Write down a balanced chemical equation for the reaction above
7. When the oxide of element H was heated with powdered Carbon, the mixture glowed and Carbon (IV) oxide was formed. When the experiment was repeated using the oxide of element J, there was no apparent reaction
(a) Suggest one method that can be used to extract element J from its oxide
(b) Arrange the elements H, J and Carbon in order of their decreasing reactivity
8. (i) Diamond and silicon (IV) Oxide have a certain similarity in terms of structure and bonding. State it
(ii) State one use of diamond
9. (a) What is allotropy?
(b) Diamond and graphite are allotropes of Carbon. In terms of structure and bonding
explain why graphite conducts electricity but not diamond
10. The diagram below shows a charcoal stove with different regions
(b) How would one avoid the production of the product at B? Give a reason for your answer
11. Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow:
(b) Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the combustion tube
12. Diamond and graphite are allotropes of carbon:-
(a) What is meant by allotropes?
(b) How do they differ in their structure and bonding
13. Study the experimental set-up below:
b) By use of a chemical equation, explain the changes that occurred in the boiling tube
c) Why was it necessary to burn the excess gas?
14. The diagram below shows the heating curve of a pure substance. Study it and answer the
questions that follow:
(d) The substance under test is definitely not water; Give a reason for this
(e) What would happen to the melting point of this substance if it were contaminated with sodium chloride?
(f) What happens to the temperature between points B and C?
15. Study the set-up below and answer the questions that follow:
(ii) State the effect of releasing gas X to the environment
(b) Write down equations for the reactions taking place in;
(i) Tube I
(ii) Tube II
(iii) Flask
(c) State the observation made in tube III
(d) Write down an equation for the reaction which could be used to generate Carbon
(IV) Oxide for the above set up
(e) Name the reagents used to generate gas x in the laboratory
(f) Complete the diagram above to show how excess gas x can be collected
16. The figure below shows the stages in the manufacture of sodium carbonate. Study the diagram
below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
(ii) Which substances are recycled in this process?
(iii) Identify the chambers in which the recycled substances are regenerated.
(iv) Name the substances U and V.
b) Give an equation for the reaction which occurs:
(i) In the reaction chamber 1
(ii) When solid V is heated.
(iii) In the reaction chamber 3.
c) State one commercial use for
(i) Sodium carbonate.
17. The set-up below was used to prepare dry carbon (II) Oxide gas. use it to answer the questions
below it:
(ii) The student produced carbon (IV) oxide gas from the reaction between Lead (II) Carbonate
and dilute hydrochloric acid. The gas was produced for a short time and the reaction came
to a stop. Explain
(iii) Write the equation for the reactions taking place in the combustion tube and the conical
flask:
Combustion tube:…………………………………………………………………..
Conical flask ……………………………………………………………………..
(iv) State one use of carbon (IV) Oxide gas apart from fire extinguisher
(v) Give two properties that make carbon (IV) Oxide to be used as fire extinguisher
(iv) State one use of carbon (IV) Oxide gas apart from fire extinguisher
(v) Give two properties that make carbon (IV) Oxide to be used as fire extinguisher
(b)
Which property of carbon (II) Oxide is demonstrated by the above equation?
(c) Aluminium carbonate does not exist. Give a reason
(d) Ammonium carbonate decomposes when heated. Write a chemical equation to
represent this decomposition
18. State and explain the observation made when a piece of charcoal is dropped in a jar containing concentrated nitric (V) acid
19. When Carbon (IV) oxide is passed through lime water, a white precipitate is formed but when excess Carbon (IV) Oxide is passed, the white precipitate disappears;
(a) Explain why the white precipitate disappears
(b) Give an equation for the reaction that takes place in (a) above
20. The set-up below was used to prepare a carbon (II) oxide gas.
(b) Complete the diagram to show how the gas can be collected
(c)Write the equation for the reaction
Sunday, 11 August 2019
Structure of the atom and the periodic table
1. In an experiment an unknown mass of anhydrous sodium carbonate was dissolved in water and the solution made up to 250cm3. 25cm3 of this
solution neutralized 20cm3 of 0.25M nitric acid.
(Na = 23.0 C = 12.0 O = 16.0)
Calculate:
(a) Moles of Nitric acid used
(b) Moles of sodium carbonate in 25cm of the solution
(c) Mass of unknown sodium carbonate used
2. Element A has atomic mass 23 and element B has atomic mass 7 and also have 12neutorns and 4 neutrons respectively.
(a) Write the electronic arrangement of A and B
(b) Which element has higher ionization energy? Explain
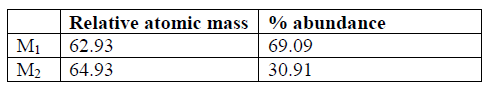
3. The table below shows the relative atomic masses and the percentage abundance of isotope M1 and M2 of element M. Calculate the relative atomic mass of element M
4. (a) Element V has two isotopes. Two thirds of V and one third of V . What is the relative atomic mass of element V?
(b) The following refers to element Y Given that isotope C contains 31 neutrons in its nucleus find the number of protons in isotope B
5. The table below shows the relative atomic masses and the percentage abundance of the isotopes L1 and L2 of element L. Calculate the relative atomic mass of element K.
6. An element M has two isotopes M and M . The relative atomic mass of the naturally occurring is 63.55. Calculate the percentage of each isotope
7. An oxide of element G has the formula as G2O3
(a) State the valency of element G
(b) In which group f the periodic table is element G?
8. The table below gives information about the ions T+ and Z2- (a) How many protons are there in the nucleus of ?
(i) Element T?
(ii) Element Z?
(b) Determine the relative formula mass of the compound formed between T and Z
(c) State two conditions under which the compound would conduct electricity
10. An ion of oxygen is larger than oxygen atom. Explain
11. Copper (II) oxide and charcoal are black solids. How would you distinguish between the two solids?
12. (a) Element X is found in period III and group IV. It consists of two isotopes 28X and QX. A sample of X was found to consist of 90% of 28X.If the relative atomic mass of X is 28.3, work out the number of neutrons in QX
(b) Draw an electrochemical cell for the above cell
13. Study the table below and answer the questions that follows:- (Letters are not the actual
symbols of element)
L3 has the highest electrical conductivity. Explain
14. Define the term melting point of a substance
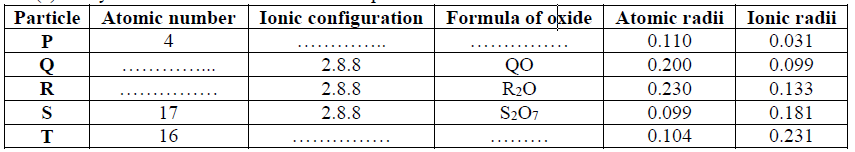
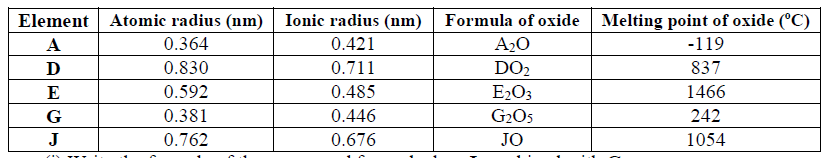
15. Use the information in the table below to answer the questions that follow. (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements).
(a) Which two letters represent the same element? Give a reason
(b) Give the number of neutrons in an atom of element R
16. The table below gives some elements in the periodic table. Use it to answer the questions that Follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements. Which of the above letters represent:
a) A metallic element which forms ions with the smallest ionic radius? Explain
b) A non metallic element with the largest bbatomic size? Explain
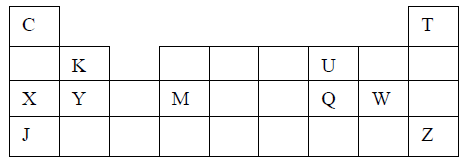
17. The grid below is part of the periodic table. Use it to answer the questions that follow: (The letters are not the actual symbols).
a) Write down the formula of the compound formed between C and A.
b) Which element has the same electron arrangement as the stable ion of:
(i) F ……………………………. (ii) A ……………………..
18. The following flow chart shows the industrial manufacture of Nitric (V) acid.
a) Identify substance B, C, E and F.
b) Describe what happens in the catalytic chamber.
c) State what takes place in chamber D.
d) 60 – 65% nitric (V) acid is produced in the absorption chamber. Describe how the acid can be concentrated.
e) State why nitric (V) acid is stored in dark bottles.
f) Copper reacts with nitric (V) acid and not hydrochloric acid. Explain.
19. The number of protons, neutrons and electrons in atoms A to F are given in the table below
the letters do not represent the actual symbol of the elements:-
(a) Choose from the table the letters that represent:
(i) An atom of a metal ..........................................................
(ii) A neutral atom of a non-metal ........................................
(iii) An atom of a noble gas ..................................................
(iv) A pair of isotopes ............................................................
(v) A cation ...............................................................................
(b) The grid below shows a part of the periodic table. The letters do not represent the actual
symbols.
Use it to answer the questions that follow:- (a) How do the atomic radius of element X and Y compare
(b) (i) Using crosses (X) to represent electrons, draw the atomic structure of element Q
(ii) State the period and the group to which element Q belong
(c) (i) The ionic configuration of element G is 2.8 G forms an ion of the type G-1.
Indicate on the grid, the position of element G.
(ii) To which chemical family does element G belong?
(iii) State one use of element U
(iv) What is the nature of the compound formed between K and U
20. (a) Study the table below and answer the questions that follow. (i) Complete the table above
(ii) From the table, choose the most reactive metal. Explain
(iii) Which element is the most electronegative. Explain
(iv) Using dots (.) and crosses (x) to represent electrons, show the bonding in the chloride of Q
(v) Explain the solubility of element T in water
(b) (i) Why is aluminium used to make utensils yet it is a reactive metal?
(ii) Distinguish between valency and oxidation number
21. a) Work out the oxidation number of phosphorous in the following compound H3PO3
b) Study the equation below:
Which species has undergone oxidation .Explain
22. The grid below represents part of the periodic table. The letters do not represent the actual
symbols of the elements. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
(a) Explain why element L appears in two different groups in the grid above
(b) State the name of the chemical family to which P and Q belong
(c) Write the formula of the compound formed between P and V
(d) Compare the melting points of Q and S. Explain
(e) Identify an element whose oxide dissolves in both acids and alkalis
(f) Write the equation for the burning of T in excess air
(g) Using dots (•) and cross (x) to represent electrons, draw a diagram to illustrate bonding in the sulphide of Q
(h) State one use of element X
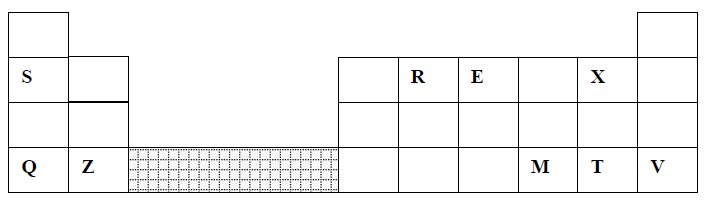
23. The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
(a) (i) Identify the element that gains electrons most readily
(ii) Which of the metal is most reactive? Explain
(iii) What name is given to the family of elements to which elements X and T belong?
(iv) Explain why:-
(I) Ionic radius of Q is larger than that of M
(II) Atomic radius of Q is greater than that of S
(v) Which of the element in the table does not have the ability to form an ionic or covalent bond? Explain
(vi) Give the formula of the compound formed between R and Z
24. The grid below is part of the periodic table. The elements are not represented by their actual symbols. Use the information to answer the questions that follow.
a) (i) Which is the most reactive
(I) Non — metal?
Explain
(II) Metal?
Explain
(ii) Name the family to which elements T and Q belongs.
(iii) Write the formula of the compound formed when W reacts with S.
(iv) Name the type of bond and structure formed when elements R and K react.
(v) Explain why element N doesn’t form compounds with other elements.
(vi) Compare the atomic radii of T and Q. Explain.
25. Study the data given in the following table and answer the questions that follow. The letters
are not the actual symbols of elements.
(i) State and explain the trend in melting point in A B C
(ii) Explain why the melting point and boiling points of element D is the highest
(iii) Explain why the element represented by letter E has two melting point values
(iv) Write down the chemical formula between element C and sulphate ions
(v) Name the chemical family in which H belong and state one use of the element
(vi) What is the nature of the oxide of the elements represented by letters C and F?
26. An element W has an atomic number 13.
a) Write the electronic configuration of the most stable ion of W
b) Write the formula of the oxide of the element W
27. Identify the particles that facilitate the electric conductivity of the following substances
(i) Sodium metal
(ii) Sodium Chloride solution
(iii) Molten Lead Bromide
28. Compare with a reason the atomic radius of Sodium to that of Aluminum.
29. Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow:
a) Write the electron arrangement of element P.
b) Give the group and period to which elements Q and R respectively.
Q ……………………………………………………
R ……………………………………………………
30. Ethanol is a liquid at room temperature but does not conduct electricity. Explain.
31. Electronic configuration for elements represented by P, Q, R and S are:-
P= 2.8.6, Q= 2.8.2, R= 2.8.1 D= 2.8.8.
(a) Select the element which forms
(i) A double charged ion
(ii) A soluble carbonate
32. The table below gives information on four elements by letters K, L, M and N. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbol of the elements.
(a) Which two elements have similar properties? Explain
(b) What is the most likely formula of the oxide of L?
(c) Which element is non-metal? Explain
33. Study the information given below and answer the questions that follow:
(i) Write the formula of the compound formed when J combined with G
(b) Explain why the melting point of the oxide of E is higher than that of the oxide of G
(Na = 23.0 C = 12.0 O = 16.0)
Calculate:
(a) Moles of Nitric acid used
(b) Moles of sodium carbonate in 25cm of the solution
(c) Mass of unknown sodium carbonate used
2. Element A has atomic mass 23 and element B has atomic mass 7 and also have 12neutorns and 4 neutrons respectively.
(a) Write the electronic arrangement of A and B
(b) Which element has higher ionization energy? Explain
3. The table below shows the relative atomic masses and the percentage abundance of isotope M1 and M2 of element M. Calculate the relative atomic mass of element M
4. (a) Element V has two isotopes. Two thirds of V and one third of V . What is the relative atomic mass of element V?
(b) The following refers to element Y Given that isotope C contains 31 neutrons in its nucleus find the number of protons in isotope B
5. The table below shows the relative atomic masses and the percentage abundance of the isotopes L1 and L2 of element L. Calculate the relative atomic mass of element K.
6. An element M has two isotopes M and M . The relative atomic mass of the naturally occurring is 63.55. Calculate the percentage of each isotope
7. An oxide of element G has the formula as G2O3
(a) State the valency of element G
(b) In which group f the periodic table is element G?
8. The table below gives information about the ions T+ and Z2- (a) How many protons are there in the nucleus of ?
(i) Element T?
(ii) Element Z?
(b) Determine the relative formula mass of the compound formed between T and Z
(c) State two conditions under which the compound would conduct electricity
9. Carbon and silicon belong to the same group of the periodic table, yet Carbon (IV) oxide is a gas while silicon (IV) oxide is a solid with a high melting point. Explain this difference
10. An ion of oxygen is larger than oxygen atom. Explain
11. Copper (II) oxide and charcoal are black solids. How would you distinguish between the two solids?
12. (a) Element X is found in period III and group IV. It consists of two isotopes 28X and QX. A sample of X was found to consist of 90% of 28X.If the relative atomic mass of X is 28.3, work out the number of neutrons in QX
(b) Draw an electrochemical cell for the above cell
13. Study the table below and answer the questions that follows:- (Letters are not the actual
symbols of element)
14. Define the term melting point of a substance
15. Use the information in the table below to answer the questions that follow. (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements).
(b) Give the number of neutrons in an atom of element R
16. The table below gives some elements in the periodic table. Use it to answer the questions that Follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements. Which of the above letters represent:
a) A metallic element which forms ions with the smallest ionic radius? Explain
b) A non metallic element with the largest bbatomic size? Explain
17. The grid below is part of the periodic table. Use it to answer the questions that follow: (The letters are not the actual symbols).
b) Which element has the same electron arrangement as the stable ion of:
(i) F ……………………………. (ii) A ……………………..
c) Element Q has atomic number 15. Indicate its position on the grid.
d) Explain how the atomic radii of the following compare:
(i) C and F
(ii) C and D
e) Write the type of bond present in a compound formed between D and A.
f) Compound C and G were completely burned in oxygen.
(i) Write down equations to show the combustion of each of the elements.
(ii) State whether each of the oxides (i) above is basic or acidic.
d) Explain how the atomic radii of the following compare:
(i) C and F
(ii) C and D
e) Write the type of bond present in a compound formed between D and A.
f) Compound C and G were completely burned in oxygen.
(i) Write down equations to show the combustion of each of the elements.
(ii) State whether each of the oxides (i) above is basic or acidic.
18. The following flow chart shows the industrial manufacture of Nitric (V) acid.
a) Identify substance B, C, E and F.
b) Describe what happens in the catalytic chamber.
d) 60 – 65% nitric (V) acid is produced in the absorption chamber. Describe how the acid can be concentrated.
e) State why nitric (V) acid is stored in dark bottles.
f) Copper reacts with nitric (V) acid and not hydrochloric acid. Explain.
19. The number of protons, neutrons and electrons in atoms A to F are given in the table below
the letters do not represent the actual symbol of the elements:-
(i) An atom of a metal ..........................................................
(ii) A neutral atom of a non-metal ........................................
(iii) An atom of a noble gas ..................................................
(iv) A pair of isotopes ............................................................
(v) A cation ...............................................................................
(b) The grid below shows a part of the periodic table. The letters do not represent the actual
symbols.
Use it to answer the questions that follow:- (a) How do the atomic radius of element X and Y compare
(b) (i) Using crosses (X) to represent electrons, draw the atomic structure of element Q
(ii) State the period and the group to which element Q belong
(c) (i) The ionic configuration of element G is 2.8 G forms an ion of the type G-1.
Indicate on the grid, the position of element G.
(ii) To which chemical family does element G belong?
(iii) State one use of element U
(iv) What is the nature of the compound formed between K and U
20. (a) Study the table below and answer the questions that follow. (i) Complete the table above
(ii) From the table, choose the most reactive metal. Explain
(iii) Which element is the most electronegative. Explain
(iv) Using dots (.) and crosses (x) to represent electrons, show the bonding in the chloride of Q
(v) Explain the solubility of element T in water
(b) (i) Why is aluminium used to make utensils yet it is a reactive metal?
(ii) Distinguish between valency and oxidation number
21. a) Work out the oxidation number of phosphorous in the following compound H3PO3
b) Study the equation below:
22. The grid below represents part of the periodic table. The letters do not represent the actual
symbols of the elements. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
(b) State the name of the chemical family to which P and Q belong
(c) Write the formula of the compound formed between P and V
(d) Compare the melting points of Q and S. Explain
(e) Identify an element whose oxide dissolves in both acids and alkalis
(f) Write the equation for the burning of T in excess air
(g) Using dots (•) and cross (x) to represent electrons, draw a diagram to illustrate bonding in the sulphide of Q
(h) State one use of element X
23. The grid below represents part of the periodic table. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
(ii) Which of the metal is most reactive? Explain
(iii) What name is given to the family of elements to which elements X and T belong?
(iv) Explain why:-
(I) Ionic radius of Q is larger than that of M
(II) Atomic radius of Q is greater than that of S
(v) Which of the element in the table does not have the ability to form an ionic or covalent bond? Explain
(vi) Give the formula of the compound formed between R and Z
24. The grid below is part of the periodic table. The elements are not represented by their actual symbols. Use the information to answer the questions that follow.
(I) Non — metal?
Explain
(II) Metal?
Explain
(ii) Name the family to which elements T and Q belongs.
(iii) Write the formula of the compound formed when W reacts with S.
(iv) Name the type of bond and structure formed when elements R and K react.
(v) Explain why element N doesn’t form compounds with other elements.
(vi) Compare the atomic radii of T and Q. Explain.
25. Study the data given in the following table and answer the questions that follow. The letters
are not the actual symbols of elements.
(ii) Explain why the melting point and boiling points of element D is the highest
(iii) Explain why the element represented by letter E has two melting point values
(iv) Write down the chemical formula between element C and sulphate ions
(v) Name the chemical family in which H belong and state one use of the element
(vi) What is the nature of the oxide of the elements represented by letters C and F?
26. An element W has an atomic number 13.
a) Write the electronic configuration of the most stable ion of W
b) Write the formula of the oxide of the element W
27. Identify the particles that facilitate the electric conductivity of the following substances
(i) Sodium metal
(ii) Sodium Chloride solution
(iii) Molten Lead Bromide
28. Compare with a reason the atomic radius of Sodium to that of Aluminum.
29. Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow:
b) Give the group and period to which elements Q and R respectively.
Q ……………………………………………………
R ……………………………………………………
30. Ethanol is a liquid at room temperature but does not conduct electricity. Explain.
31. Electronic configuration for elements represented by P, Q, R and S are:-
P= 2.8.6, Q= 2.8.2, R= 2.8.1 D= 2.8.8.
(a) Select the element which forms
(i) A double charged ion
(ii) A soluble carbonate
32. The table below gives information on four elements by letters K, L, M and N. Study it and answer the questions that follow. The letters do not represent the actual symbol of the elements.
(b) What is the most likely formula of the oxide of L?
(c) Which element is non-metal? Explain
33. Study the information given below and answer the questions that follow:
(b) Explain why the melting point of the oxide of E is higher than that of the oxide of G
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)