(i) Write an equation for the reaction that takes place
(ii) Why is it necessary to have a hot nichrome wire in the gas jar?
(iii) Write the formula of the complex ion formed when excess ammonia gas is passed through
a solution containing Zn2+ ions
(ii) Why is it necessary to have a hot nichrome wire in the gas jar?
(iii) Write the formula of the complex ion formed when excess ammonia gas is passed through
a solution containing Zn2+ ions
2. The diagram below shows the catalytic oxidation of ammonia gas. Use it to answer the
questions that follow:-
(a) What metal could rod M be made of?
(b) State and explain two observations made inside the conical flask
3. Ammonia gas is prepared in the laboratory by the action of an alkali on an ammonium salt. A student wanted to prepare a sample of ammonia gas in the laboratory. (a) Give one alkali that can be used in the above experiment
(b) Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the above experiment
4. (a) Explain the importance of the high percentage of nitrogen in air
(b) Why is nitrogen used for storage of semen in artificial insemination?
5. The diagram below is used in preparation of a gas in the laboratory. Answer the questions that follow;
(b) State one physical property which makes it possible for the gas to be collected as shown
(c) State one commercial use of gas X
6 Study the flow charts below and use them to answer the questions that follow:
(i) Solution A
(ii) Solution B
(b) State and explain the observations made when a sample of dry white precipitate B is
heated in a test-tube
7. The set-up below is an arrangement showing how metals react with nitrogen (IV) oxide.
Study it and answer the questions that follow:-
(a) Nitrogen (IV) oxide is passed through the combustion tube before copper is heated. Give a reason for thisStudy it and answer the questions that follow:-
(b) State the observations that would be made at the end of the experiment in the combustion tube
(c) Name gas N ……………………………………………………………………..
8. (a) In haber process hydrogen and nitrogen react in the presence of finely divided iron catalyst. Explain why the catalyst is finely divided
(b) A mixture of N2, H2 and NH3 was bubbled through 0.2M hydrochloric acid solution. The final concentration of the acid was found to be 0.1M. Give explanation
9. In an experiment, a few drops of concentrated nitric acid were added to aqueous iron II sulphate in a test-tube. Excess ammonia solution was then added to the mixture
(a) State the observations that were made when:-
(i) Concentrated nitric acid was added to aqueous iron (II) sulphate
(ii) Excess ammonia was added to the mixture
(b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction which occurred in a (ii) above
10. The chart below shows a summary for the preparation of nitrogen gas from air
(b) Write an equation for the reaction taking place in chamber II
(c) The nitrogen gas obtained is not pure. Explain
11. Dilute nitric acid is added to excess green solid. Effervescence occurs and a blue solution is formed. When excess ammonia solution is added to a sample of the solution a deep blue solution is formed
(a) Identify the anion and cation in the green solid:
(b) Write an ionic equation for the reaction forming deep blue solution
12. The diagram below is a set-up for preparation and collection of a gas. Study it answer the questions that follow:
(ii) Write an equation for the formation of gas X
(iii) What precaution should be observed when preparing gas X by the above method?
(iv) Describe the suitable drying agent for gas X
(v) How can one confirm that the gas collected is gas X?
(vi) State two physical properties of gas X
(b) The diagram below is a set-up used in preparation of ammonia solution. Study it and answer
the questions that follow (i) What is the purpose of the filter funnel in the set-up above?
(ii) What would happen if a delivery tube was used in place of the filter funnel?
(iii) What observation would be made on litmus paper placed into the solution in the beaker at the end of the experiment?
13. The following flow chart shows the industrial manufacture of Nitric (V) acid.
a) Identify substance B, C, E and F.
b) Describe what happens in the catalytic chamber
d) 60 – 65% nitric (V) acid is produced in the absorption chamber. Describe how the acid can be concentrated.
e) State why nitric (V) acid is stored in dark bottles.
f) Copper reacts with nitric (V) acid and not hydrochloric acid. Explain.
14. The flow chart below illustrates two industrial processes, Haber process and the Contact process:
(i) Give the name of the process by which air is seperated into oxygen and nitrogen(ii) Apart from oxygen and nitrogen gases produced from process (a)(i) Name one other gas produced
(b) Name the substances represented by the letters A, B, C and E
(c) Name the catalysts used in:
(i) Haber Process ……………………………………………………………………..
(ii) Contact Process ……………………………………………………………………..
(d) Explain the role of the catalysts in both the Haber and the Contact processes
(e) Write a chemical equation for the formation of compound B
(f) Calculate the percentage by mass of the nitrogen present in compound D
(g) Give one major use of compound E
15. The diagram below represents a set-up used to obtain nitrogen from air. Study it and
answer the questions that follow:-
(ii) What is the purpose of sodium hydroxide
(iii) Write an equation for the reaction which took place in tube “P”
(iv) Give the name of one impurity in the nitrogen gas obtained
(v) Give a reason why liquid nitrogen is used for storage of semen for artificial insemination
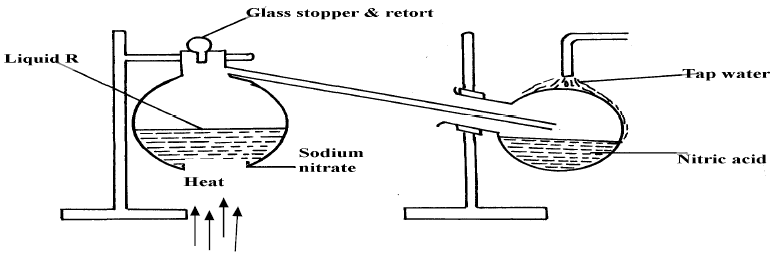
(b) The set-up below was used to prepare nitric acid.
(i) Give the name of liquid ‘R’ .........................................................................
(ii) Explain the following:-
(a) Nitric acid is stored in dark bottles
(b) The reaction between copper metal with 50% nitric acid in an open tube gives brown fumes
16. Study the flow chart below and answer the questions which follow:
(a) Nitrogen gas ………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) Hydrogen gas …………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) State three conditions required in process I
(iii) Name: catalyst P…………………………………………………………………
Gas M……………………………………………………………………..……
(iv) Write chemical equations for;
(a) Formation of gas M
(b) The reaction in the absorption tower
(v) Give two reasons why step IV is necessary
(vi) Describe how you would test if a given liquid is a nitrate
(vii) Give three uses of nitric acid
17. The diagram below shows the apparatus for the laboratory preparation of one of the oxides
of Nitrogen
(ii) Write the equation for the thermal decomposition of ammonium Nitrate
(iii) The gas is being collected over hot water. Explain
(iv) State and explain the observations made when burning sulphur is lowered into a gas jar containing the gas
(b) (i) Name the catalyst used during catalytic oxidation of ammonia
(ii) Nitrogen (IV) oxide is the final product during catalytic oxidation of ammonia. Write a chemical equation for its formation
(iii) State two physical differences between Nitrogen (I) oxide and Nitrogen (IV) Oxide
(c) Nitric acid is prepared in the laboratory by action of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid on a suitable Nitrate and distilling off the Nitric acid, in all glass apparatus.
(i) Why must the apparatus be made of glass?
(ii) Hot concentrated Nitric acid reacts with sulphur in the equation below:-
(I) Identify the species :-
Oxidised ………………………… Reduced …………………………………
(II) Pure nitric acid is colourless but the product during its preparation is usually pale yellow.
Explain
18. a) Describe the process by which oxygen can be obtained from air on large scale
b) The flow chart below shows the industrial manufacture of nitric (V) acid i) Identify substances X and Y
ii) Write an equation for the reaction taking place in the absorption tower
iii) The concentration of the acid obtained is about 60%. How can this concentration be increased to about 65%?
iv) A factory uses nitric (V) acid and ammonia as the only reactants for the production of a fertilizer. If a mass of 9600kg of fertilizer was produced, calculate the mass of ammonia gas needed
(N = 14, H = 1, O = 16) (a) Name another substance which can be used instead of sodium hydroxide
(b) What is the function of filters?
(c) Identify the substance removed at step III
(d) At what temperature does liquid oxygen distil?
(e) Identify process X
(f) Describe how process X occurs
(g) I. State one industrial use of Nitrogen
(II) Air is a mixture but not a compound. Give two reasons
20. Using chemical equations show the bleaching actions of chlorine and sulphur(IV)oxide
21. The diagram below represents an in complete set-up for preparation of a dry sample of gas R
b) Write a chemical equation for the reaction that produces gas R
22. The diagram below was used to investigate the reaction between nitrogen(I)oxide and copper
turnings. Study it and answer the questions that follow: a) What has been omitted in the set-up? (show it on the diagram)
b) Write a chemical equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube
c) State one use of gas P
23. When sulphur powder is heated to over 400oC the following changes are observed:- At 113oC it melts into light brown liquid. The liquid then darkens to become reddish-brown and very viscous at 160oC. Above 160oC the liquid becomes almost black. At the boiling point the liquid becomes mobile. Explain these observations
24. Concentrated sodium chloride (Brine) was electrolysed using platinum electrodes.
What would be the difference in terms of products at each electrode if dilute sodium chloride
solution was used in place of brine. Explain
25. (i) Nitrogen (I) Oxide supports, combustion of burning charcoal. Write an equation
to show this reaction
(ii) Ammonium nitrate can be heated to give off nitrogen (I) Oxide. However, a mixture
of NH4Cl and NaNO3 is preferred. Explain
(iii) Ammonia turns wet red litmus paper blue. Which ion is responsible for this reaction
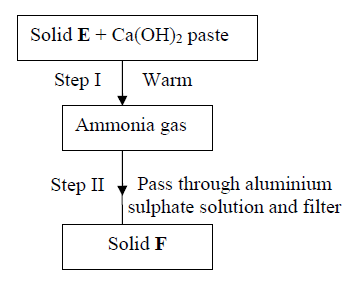
26. Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow:
(b) Write down a balanced equation for the reactions that lead to formation of solid F
27. When a few drops of aqueous ammonia were added to a colourless solution X, a white
precipitate was formed. On addition of more aqueous ammonia, the white precipitate
dissolved to a colourless solution Q
(a) Name the white precipitate formed
(b) Write formula of the complex ion present in the colourless solution Q
28. The first step in the industrial manufacture of nitric cid is the catalytic oxidation of ammonia gas.
a) What is the name of the catalyst used?
b) Write the equation for the catalytic oxidation of ammonia gas.
c) Nitric acid is used to make ammonium nitrate. State one use of ammonium nitrate.
29. Explain what is observed when ammonia gas is bubbled into Copper (II) sulphate solution till in excess.
30. (a) State the conditions under which nitrogen react with hydrogen to form ammonia during Haber process
(b) When dry ammonia gas is passed over hot copper (II) Oxide, a shinny brown residue and a colourless droplets are formed. Explain these two observations
(b) When dry ammonia gas is passed over hot copper (II) Oxide, a shinny brown residue and a colourless droplets are formed. Explain these two observations
31. Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
(b) Identify:-
(i) Gas A ………………………………………….………
(ii) Liquid B ………………………………..…………………






























Patrick
ReplyDeleteAmmonium Bisulfite Catalyst - Shakti Chemicals is offering ammonium bisulfite catalyst with high quality services. If you want Ammonium Bisulfite Catalyst then please Contact Us: 9825043369
ReplyDeleteAnswer
ReplyDeleteAnswers to all the questions
ReplyDelete